Introduction to Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
As the world continues to pivot towards renewable energy and sustainable practices, Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are becoming increasingly crucial in modern power grids. BESS technology not only enhances the stability and reliability of energy supply but also facilitates the effective integration of renewable energy sources.
What is BESS?
A Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) is a technology that uses batteries to store electrical energy for later use. It consists of various components, including a set of batteries, an inverter, and a control system. By converting electrical energy from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) using an inverter, BESS can efficiently store and distribute energy as needed.<\/p>

This image illustrates how Battery Energy Storage Systems are often housed in container-like structures, making them easy to configure and transport as needed.
The Importance of BESS
BESS plays a vital role in stabilizing the power grid. With the inherent variability of renewable sources like solar and wind, BESS helps store excess energy generated during peak production times. This energy can then be dispatched during periods of increased demand or when renewable output is low, thus ensuring a steady and reliable power supply.
Types of BESS Technologies
Batteries used in BESS vary, with lithium-ion being the most widespread due to their high energy density and efficiency. Other technologies, such as flow batteries, offer long cycle life and scalability, making them suitable for different applications.<\/p>
Applications of BESS
BESS is used across residential, commercial, and utility-scale settings, offering a wide range of applications like peak shaving, load leveling, and emergency backup. Whether it’s ensuring uninterrupted power supply during outages or minimizing electricity costs during peak hours, BESS proves indispensable.
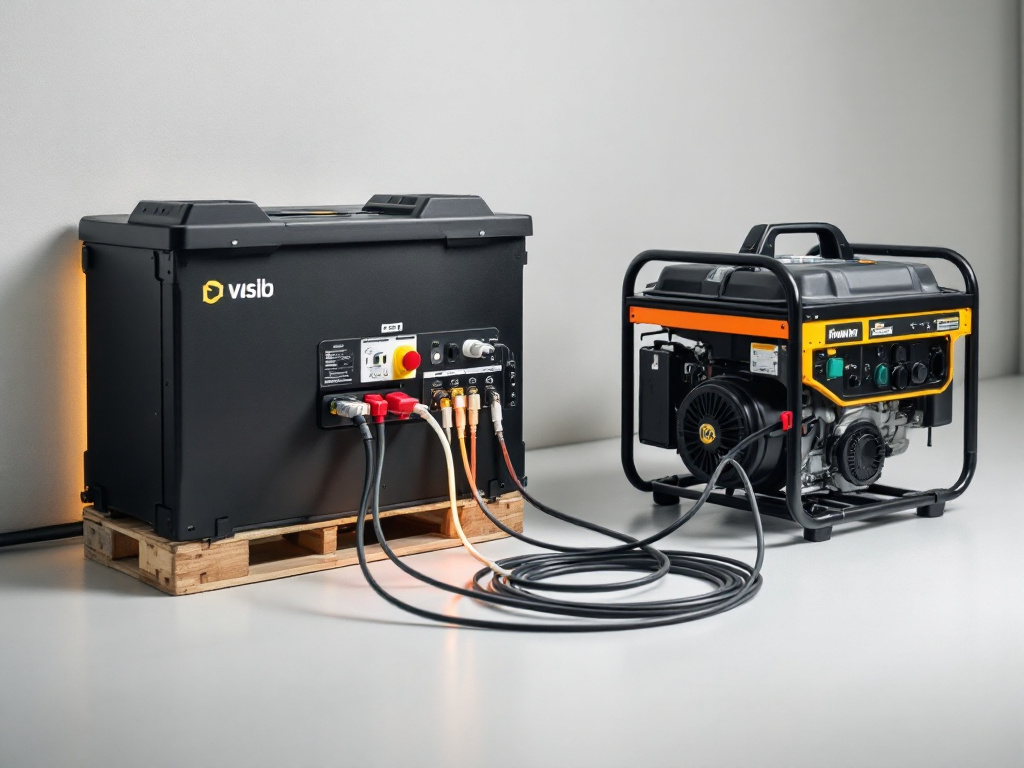

This setup showcases the seamless integration of a battery box with a generator, highlighting the adaptability of BESS in different scenarios, including backup power solutions.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their benefits, BESS comes with challenges such as initial installation cost, battery lifespan, and environmental impact related to battery disposal. Safety is another critical consideration, as improper handling can result in hazardous situations.
Conclusion
Battery Energy Storage Systems are an integral part of modern energy strategies, providing essential support for renewable energy integration and grid stability. With ongoing advancements in technology and decreasing costs, BESS will likely play an even more significant role in the future of energy systems.